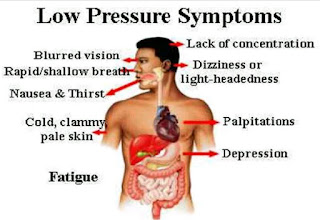
Low blood pressure or hypotension is an abnormal medical condition in which an individual's blood pressure is abnormally lower than 90/60mmHg. A sudden drop in blood pressure can be very dangerous because the body can't bring blood pressure back to normal or can't do it fast enough and this can restrict the amount of blood flowing to the brain and other vital organs which can cause unsteadiness, dizziness or fainting.
Increased vascular elasticity with or without reduced vascular resistance
Other factor:
Increased coronary artery elasticity
Types of low blood pressure
- Low blood pressure on standing up (orthostatic hypotension) This is a sudden drop in blood pressure when you stand up from a sitting position or from lying down, such persons may experience dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision and even fainting, this happens because enough blood did not return to the brain immediately after standing up. Orthostatic can occurs for reasons such as dehydration, prolonged bed rest, pregnancy, diabetes, heart problem, excessive heat etc
- Low blood pressure after eating (postprandial hypotension) This sudden drop in blood pressure after eating affects mostly older adults who are likely to have high blood pressure or autonomic nervous system disorders such as Parkinson's disease
- Low blood pressure from faulty brain signals (neurally mediated hypotension) This disorder causes a blood pressure drop after standing for a long period, it occurs because of miscommunication between the heart and the brain, young adults and children are mostly at risk
- Low blood pressure due to nervous system damage: It is a rare disorder that causes progressive damage to the autonomic nervous system
Patients who experience associated side effects such as dizziness, lightheadedness and excessive thirst need to be further investigated, these symptoms are a results of hypoperfusion of vital organs, which can lead to organ damage in the long run. In more serious cases patients may faint, it can also confine one to bed and sudden drop in blood pressure can be life threatening.
Causes of low blood pressure
Hypotension can be caused by a change in either the cardiac output or pulmonary vascular resistance, this can be the result of drugs or combination of drugs
- Severe dehydration
- Reaction to alcohol or medication
- High blood pressure
- Low blood temperature
- Heart muscle disease
- Loss of bloodblood
- Lack of nutrients in diet
Low blood pressure table
Blood pressure is a measurement of the pressure in the arteries during the active and resting phases of each heart beat.
Systolic pressure:- this is the top number in the BP reading, it is the amount of pressure the heart generate when pumping blood through the arteries to the rest of the body
Diastolic pressure:- it is the bottom number in the blood pressure reading, it refers to the amount of pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Treatment
- Chilly pepper
- Alligator pepper
- Salty food (confirm with your doctor)
- Enough sleep
- Water
- Acupuncture therapy
- Acupuncture therapy
Healthy tips
- Get adequate sleep
- Increase your water intake
- Reduce stress
- Practice breathing techniques
- Do regular exercise to promote blood flow
- Avoid prolong standing
- Avoid alcoholic beverages
- Avoid heavy lifting
Low blood pressure can deprive your body of enough oxygen to carry out it's normal functions leading to damage to your heart and brain.
It is health that is real wealth
It is health that is real wealth